
This article was last updated on April 16, 2022
Canada: ![]() Oye! Times readers Get FREE $30 to spend on Amazon, Walmart…
Oye! Times readers Get FREE $30 to spend on Amazon, Walmart…
USA: ![]() Oye! Times readers Get FREE $30 to spend on Amazon, Walmart…Back in 2012 during one of the endless crises between Israel and Palestine, I looked at background information about the Qassam rocket, the response of Palestine to Israel's military might. I'd like to update that posting to help us better understand one half of the current hostilities.
Oye! Times readers Get FREE $30 to spend on Amazon, Walmart…Back in 2012 during one of the endless crises between Israel and Palestine, I looked at background information about the Qassam rocket, the response of Palestine to Israel's military might. I'd like to update that posting to help us better understand one half of the current hostilities.
As background, let's look at a graph from the Israeli Defense Forces blog showing the number of rocket attacks against Israel from the Gaza before the beginning of Operation Protective Edge on July 7, 2014:
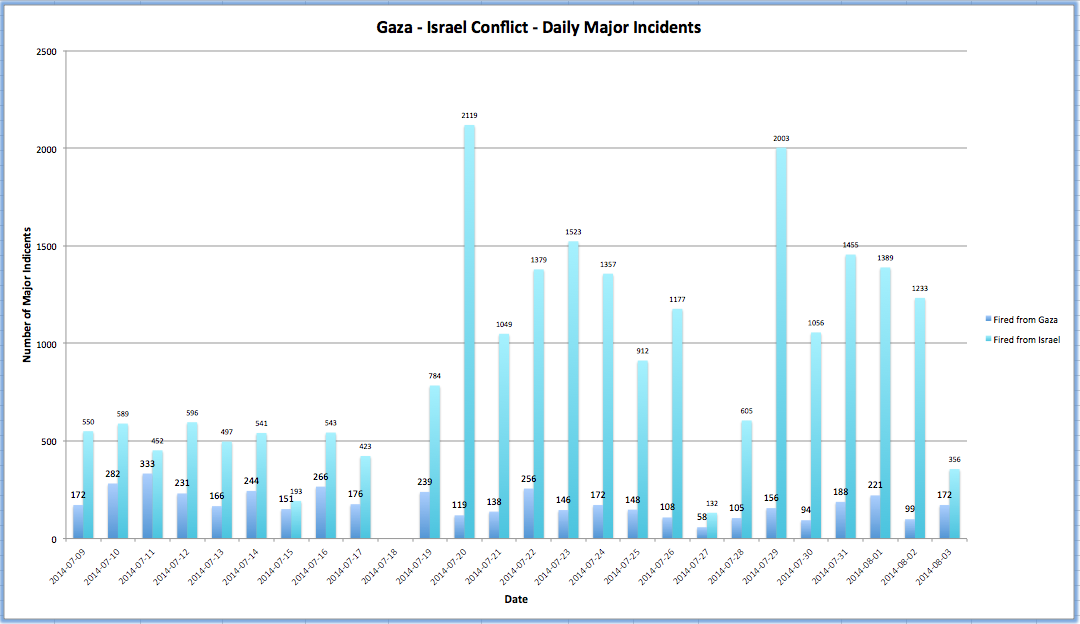
The IDF notes that more than 11000 rockets have been fired from the Gaza since 2005 and a total of 15,200 since 2001. Here is a graph showing the munitions count from both sides since July 9, 2014:
According to Mondoweiss, here is a list of all victims of Hamas rocket and mortar attacks since 2004:
As I noted in my previous posting, Hamas first used Qassam rockets on March 5, 2002. The original Qassam rockets were essentially a homemade projectile with a cast iron, steel or aluminum tube as a body, a small finned section at the tail containing an impact detonator and a small warhead, armed with TNT. The fuel used to propel these rockets is a mixture of melted glucose (sugar) and commercial grade fertilizer brought in from Israel. The rockets have no guidance system so their flight path can be rather unpredictable. The source materials for these earlier rockets cost a mere $650. The rockets are very easily transported and can be launched from truck mounted launchers or wooden scaffolding. Their mobile nature makes it easy for Hamas to quickly launch these rockets and leave the area before they are intercepted by the Israeli Defense Forces.
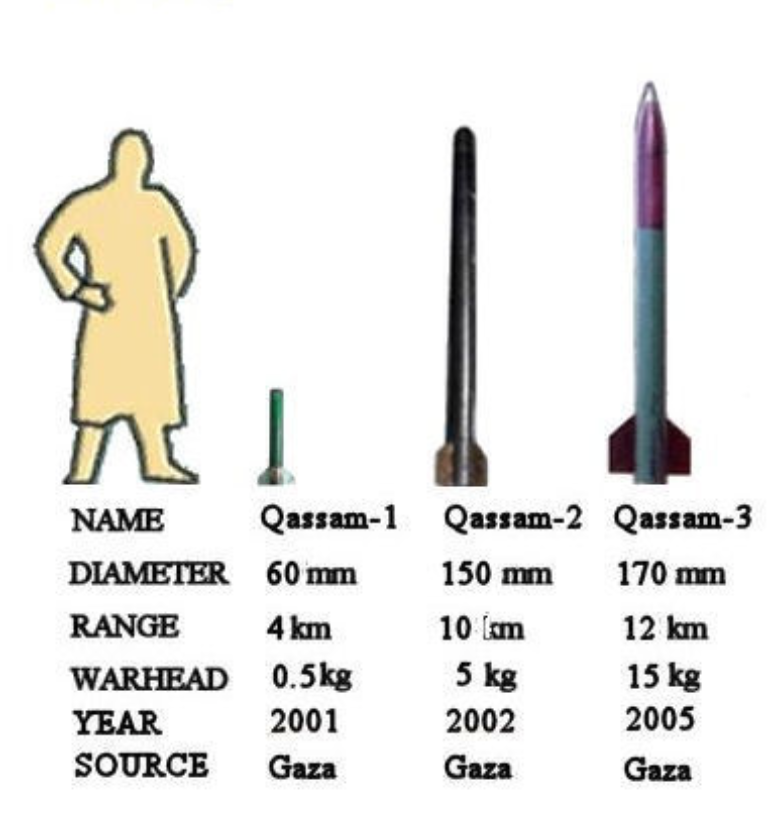
Here is a graphic showing the three types of Qassam rockets, their range and the size of their warhead:
In 2008, Hamas began to use the Grad rocket, a Russian-designed rocket with a range of up to 21 kilometres and a warhead of 18 kilograms, slightly larger than the Qassam 3. It is the world's most widely used multiple rocket system, first appearing in 1963. It is used in more than 30 nations around the world. It is believed that Hamas sourced its Grad rockets from Iran and This rocket can be fired from a truck mounted multiple launch system which has a capacity of 40 rockets as shown on this video:
The launching vehicle can be prepared to fire in as little as three minutes and can be packed up a ready to move in two minutes after firing. A full salvo of rockets can cover an area of between 0.8 and 1.0 hectares or around 2 acres. The launcher is reloaded manually in seven minutes.
While it was believed that Hamas did not have the capability to fire multiple Grad rockets, the IDF claims that it discovered multiple Grad launchers at a school in Gaza as shown on this video:
In late November 2012, Hamas showed the world that it had increased its rocket capabilities, using the Iranian Fajr-5 artillery rocket for the first time. This rocket has a range of about 75 kilometres and brought both Tel Aviv and Jerusalem within range. The Fajr-5 is much heavier and larger than the Qassam family, being about 6 metres (20 feet) tall
The Khaibar-1, also known as the M-302, a Syrian-built (from a possible Chinese design for the 302 mm WS-1) missile, has also been used. This 302 millimetre missile, first introduced in 2006, has a range of up to 212 (132 miles) kilometres which means that Hamas can target the northern coastal city of Haifa. This missile is at least 5 metres (16 feet) long, weighs 524 kilograms (1155 pounds) and has a warhead that weights 175 kilograms (386 pounds). It can be launched from a truck-mounted multiple rack-type rocket launcher that can handle four or six missiles at a time. Its accuracy is considered poor since it has no guidance system. It was also used by Hezbollah in 2006 during the Second Lebanon War. Here is a photograph of the similar WS-1 302 mm Multiple Rocket Launch System:
Apparently, Iran began to ship missiles to Gaza shortly after the 2012 hostilities ended. A shipment of Syrian Khaibar-1 M-302s was intercepted in the Red Sea off the Sudan-Eritrean border aboard the Panamanian-registered Klos-C in March 2014 as shown on this video:
It is believed that the rockets were shipped from Syria to Iran and destined for Sudan where they would be taken by land through Egypt to Gaza. Despite this, it is still believed that Hamas possesses additional supplies of M-302 rockets, produced in Syria.
To summarize, here is a map from the Missile Threat website showing the range of the Hamas inventory of rockets and missiles:
Here is a map from Global Security showing the warning times from rocket launch to strike:
At the outset of hostilities in 2014, Israeli Intelligence Minister Yuval Steinitz estimated that Hamas had about 10,000 rockets in its inventory. By the end of July 2014, he announced that 2600 rockets had been fired and a further 3000 had been destroyed by the IDF. The fact that Hamas now has the capability of striking terror far into the heart of Israel is creating a situation of fear among Israelis who formerly were immune from Hamas' rocket attacks.
Click HERE to read more of Glen Asher's columns
You can publish this article on your website as long as you provide a link back to this page.






Be the first to comment