The newest asset class on the block has its roots in the American housing market crash. Since October 2013, billions of dollars have been invested in REO-to-rental securities where the income stream is sourced from the rent cheques of thousands of tenants in single-family dwellings. In case you have forgotten or were not aware, REO stands for Real Estate Owned, a type of property that is owned by a lender, either a government agency or a bank usually after an unsuccessful attempted sale. As we have found out from the recent past, if there's a dollar to be made, Wall Street will find a way to get in on the action. Damn the torpedoes, it's full steam ahead when there are millions of dollars in commissions to be made.
Wall Street’s Newest Asset Class – Rental Income Bonds
Over the past two years, investors (mainly corporate) have acquired more than 200,000 homes for a $20 billion plus investment; most of these homes were foreclosures that are now being rented by families that struggled to find affordable housing after the real estate market collapse, most particularly, those millions of families that were unceremoniously booted from their homes as their mortgages went way underwater at the same time as they found themselves under- or unemployed According to Realtytrac, in September 2013, institutional investor purchases represented a whopping 12.1 percent of all home sales with some markets like Memphis seeing rates of up to 25.4 percent and Atlanta at rates of up to 23 percent. By securitizing the loans that REO-to-rental firms have used to buy these foreclosures, packaging them up and selling them to investors, the firms are allowed to continue to buy additional properties with the proceeds at the same time as their bondholders get stream of cash flow from the rental income.
Let's get a sense for how big this new asset class has become. Back in 2013, Blackstone Group offered the first bond backed by rental income from single family homes. The triple-A rated bond (now there's a shock) was secured by individual mortgage liens on each underlying property. The total offering was $479 million. Blackstone was spending more than $100 million a week to buy homes in 14 U.S. cities and between April 2012 and March 2014, purchased 43,000 homes for a total investment of $8 billion. Another rental income bond was issued in March 2014 by Colony Capital Markets who came to market with $500 million in securities. According to Housingwire, American Residential is set to bring a triple-A rated $342.67 million securitization on 2880 rental properties to market along with Silver Bay Realty and their $312.67 million offering on 3089 single-family homes. Invitation Homes has brought three REO-to-rental securitization to market; $322.58 million in triple-A bonds, $78.79 million in double-A rated bonds and $69.41 million in single-A rated bonds. This is Invitation Homes third kick at the rental securities can; the company now has nearly $1 billion in REO-to-rental securities outstanding. In total, some experts anticipate that the market for REO-to-rental securities is currently about $3 billion and could grow by another $10 to $15 billion over the next few years.
The gentleman who is credited with coming up with this rental-backed securities scheme, Lewis Ranieri, assures investors that rental-backed bonds offer no risk to investors because they are backed by a steady flow of rental income and that investors will not see a repetition of the implosion of the mortgage-backed securities market. Others disagree. A coalition of housing and economic rights advocates, HERA, sent the following letter to Janet Yellen, The Department of Housing and Urban Development, the Securities and Exchange Commission and the Office of the Comptroller of Currency (among others):
The letter, which was signed by 75 housing and consumer advocacy groups, opens with:
"This letter is sent on behalf of the undersigned organizations concerning a serious and still growing problem – the creation of another housing bubble, the displacement of tenant and homeowner households, and the destabilization of neighborhoods as a result of failed and negligent federal policies. Such policies and inaction have enabled Wall Street and other cash investors to outbid first time homebuyers, displace tenants, and alter the fabric of local communities."
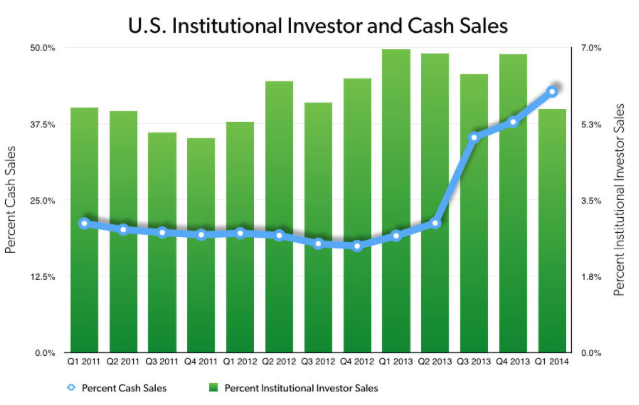
They note that in one community (East Palo Alto), almost half of rental housing stock is controlled by a single company. As well, they note that the preference for cash deals has locked out many potential owners with cash deals making up 42.7 percent on total home sales in the first quarter of 2014 as shown on this graph:
Obviously, the stricter lending standards imposed on potential individual mortgagees has made it increasingly difficult for individual buyers to meet the cash offers that large institutions can make to sellers.
The authors go on to note:
"At the same time, we are poised to experience another crisis if federal regulators fail to recognize and take corrective action to address red flags that are all too familiar: inflated housing prices, the explosion of securitized housing payments, undue challenges facing homeowners unable to secure the lowest priced loan product for which they qualify, and actions of GSEs that are more focused on profit motive than serving their affordable housing mission.
A new kind of landlord is buying properties in bulk—hedge funds, private equity firms and other companies that have not been in the rental business for very long, do not have an interest in abiding by their legal duties as landlords, and do not calculate any incentive to being good landlords. These investor groups have a focus on turning a dollar, but have no connection to the community in which they are investing. The continued transfer of capital to investors via REO bulk sales now facilitates the creation of a new rental securitization market that benefits the very industry that caused the subprime loan crisis. And the market is growing to an estimated trillion dollars." (my bold)
Red flags indeed.
Obviously, the biggest issue facing all of these institutional landlords is the same issue that faces individual landlords; a potential increase in vacancy rates This problem exists for all companies involved in this business since it is far easier and much cheaper for renters to walk away from a lease than it is to walk away from a mortgage. The volatility of rental markets varies greatly from city-to-city and from year-to-year and companies that rent homes for a living have to find ways to limit renter turnover and keep vacancy rates low. This is why some experts are questioning the triple-A rating given to this new class of securities.
There is no doubt that this little game has stabilized America's housing market (i.e. putting an artificial price floor in place) and prevented the continuing free fall of housing prices in some selected markets but at what cost? Unfortunately, it has meant that hundreds of thousands of tenants who would like to buy a home are now being squeezed out of the housing market by institutional investors, leaving them with little choice but to continue to rent from the same corporations that are squeezing them out of the real estate market. Reports suggest that REO properties are being held off the market by banks and other mortgage servicers to ensure that demand exceeds supply, artificially driving up housing prices, making it particularly difficult for American families that have seen their incomes stall at pre-Great Recession levels.
Obviously, like the skewed unemployment data that we are fed every month, the housing market data that we see on a monthly basis has been skewed by the entry of Wall Street and the corporate world through hedge and private equity funds into certain housing market at levels never seen before.
Click HERE to read more of Glen Asher's columns
You can publish this article on your website as long as you provide a link back to this page.










Be the first to comment