I recently posted an article on the unintended consequences that central bank actions have had on the global bond market. According to a recent poll by the CFA Institute, 30 percent of all respondents believed that all of the fixed-income markets are experiencing an asset bubble with an additional 24 percent believing that there is a bubble in sovereign bonds and at least one other class of bonds, either high-yield bonds or investment-grade corporate bonds. This should be of great concern to investors, both individual and institutional, because even a small increase in interest rates in the current low-yield environment will have a significant negative impact on bond prices. This will result in painful capital losses for all bond investors who have been chasing yields down to near-zero or sub-zero levels. A recent analysis by Fitch looks at just how painful this revaluation could be for sovereign bond investors.
As we all know, there are two factors at work in the world's bond markets:
1.) the use of unconventional monetary policies implemented by the Federal Reserve, Bank of Japan and central banks throughout Europe that have kept interest rates at or below zero for an extended period of time. By July 15, 2016, a total of $11.5 trillion in sovereign bonds were trading at a negative yield.
2.) the flight to safety by investors since the Great Recession which has pushed up demand for sovereign bonds, resulting in higher prices and lower yields.
The bonds that are most sensitive to changes in interest rates are longer-term bonds; even a small change in interest rates has a significant impact on bond prices given that the life of the bond is very long.
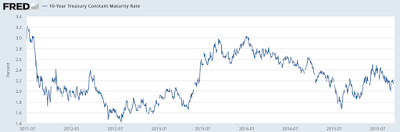
The analysis by Fitch looks at what has happened to bond yields over the five year period from July 2011 to July 2016. Let's look at a small sample of ten-year bonds from around the globe. Here's what has happened to the yield on ten-year Treasuries over the five year period:
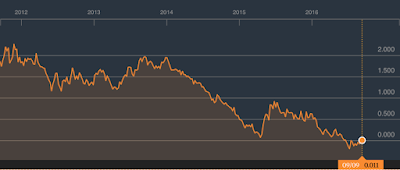
Here's what has happened to the yield on ten-year German bunds over the five year period:
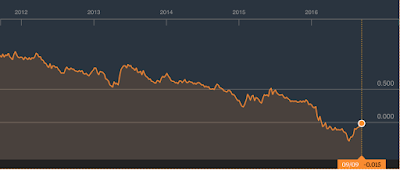
Here's what has happened to the yield on ten-year Japanese bonds over the five year period:
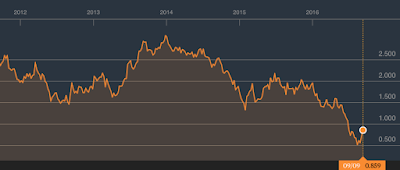
Here's what has happened to the yield on ten-year United Kingdom gilts over the five year period:
According to Fitch's analysis, the median yield on ten-year sovereign bonds is 270 basis points lower than it was in July 2011 and the median yield on one-year sovereign bonds is 176 basis points lower than it was five years ago.
Now, let's get to the painful part of Fitch's analysis. Using the yields from July 2011 to reprice current sovereign debt, Fitch calculates that there would be aggregate sovereign bond market losses of $3.8 trillion across 2500 securities. Losses would be greatest for investors who hold European sovereign bonds and losses would be as follows:
Italy – 21 percent
Spain – 21 percent
United Kingdom – 19 percent
For investors holding sovereign debt with maturities of 25 years or more, on average, investors in European countries would lose 44 percent of the market value of their securities.
It is important to note that the pace of the rise in interest rates is key to the size of the losses; a slower tightening by the world's central banks would result in less significant losses than a sudden increase in interest rates.
So much for that flight to safety! Thanks to the long-term monetary policy experiment by the world's central banks since the Great Recession, investors in what used to be the lowest risk investments could see the value of their assets unexpectedly plummet in value.
Click HERE to read more of Glen Asher's columns
You can publish this article on your website as long as you provide a link back to this page.

Be the first to comment